
VMware vSphere Bitfusion. Download Product Drivers & Tools Download Trial; VMware vSAN. Download Product Drivers & Tools Download Trial Get Training; VMware vSphere Data Protection Advanced. Download Product Drivers & Tools Get Training; VMware vSphere Storage Appliance. Download Product Drivers & Tools; VMware vSphere. Run any app on any cloud on any device with a digital foundation built on VMware solutions for modern apps, multi-cloud, digital workspace, security & networking. Functional cookies help us keep track of your past browsing choices so we can improve usability and customize your experience. These cookies enable the website to remember your preferred settings, language preferences, location and other customizable elements such. VMware vSphere is VMware's virtualization platform, which transforms data centers into aggregated computing infrastructures that include CPU, storage, and networking resources. VSphere manages these infrastructures as a unified operating environment, and provides you with the tools to administer the data centers that participate in that environment.
With vSphere 6.0 the vCenter Virtual Server Appliance (VCSA), now has a component called the Platform Services Controller (PSC). The PSC handles things like SSO and the License Server and ships with its own Certificate Authority called VMware Certificate Authority (VMCA). In this blog post we’ll quickly go over some of the modes of VMCA operation and how to download and install the VMCA root certificate into your browser.
VMCA overview
VMCA issues certificates for VMware solution users, machine certificates for machines on which services are running, and ESXi host certificates. Host provisioning happens when the ESXi host is added to vCenter Server explicitly or as part of the ESXi host installation.
VMware Endpoint Certificate Store (VECS) serves as a local (client-side) repository for certificates, private keys, and other certificate information that can be stored in a keystore. You can decide not to use VMCA as your certificate authority and certificate signer, but you must use VECS to store all vCenter certificates, keys, and so on. ESXi certificates are stored locally on each host and not in VECS. VECS runs on every embedded deployment, Platform Services Controller node, and management node and holds the keystores that contain the certificates and keys.
With VMCA you can deal with certificates in three different ways. For the purposes of discussion we’ll call them
- VMCA Default
- VMCA Enterprise
- Custom
VMCA Default: VMCA uses a self-signed root certificate. It issues certificates to vCenter, ESXi, etc and manages these certificates. These certificates have a chain of trust that stops at the VMCA root certificate. VMCA is not a general purpose CA and its use is limited to VMware components.
VMCA Enterprise: VMCA is used as a subordinate CA and is issued subordinate CA signing certificate. It can now issue certificates that trust up to the enterprise CA’s root certificate. If you have already issued certs using VMCA Default and replace VMCA’s root cert with a CA signing cert then all certificates issued will be regenerated and pushed out to the components.
Custom: In this scenario VMCA is completely bypassed. This scenario is for those customers that want to issue and/or install their own certificates. You will need to issue a cert for every component, not unlike you do today for 5.5 when using 3rd party certs. And all of those certs (except for host certs) need to be installed into VECS.
In Default and Enterprise modes VMCA certificates can be easily regenerated on demand.
Important: For vSphere 6.0 the procedure for installing these certificates has changed from vSphere 5.x. In order to make this procedure less painful a new Certificate Manager tool is shipped as part of vCenter for Windows and VCSA. It will be located here:
Windows: C:Program FilesVMwarevCenter Servervmcad certificate-manager
Linux: /usr/lib/vmware-vmca/bin/certificate-manager
The procedure will be fully documented and will be the topic of a future blog article.
Downloading VMCA’s Root Certificate
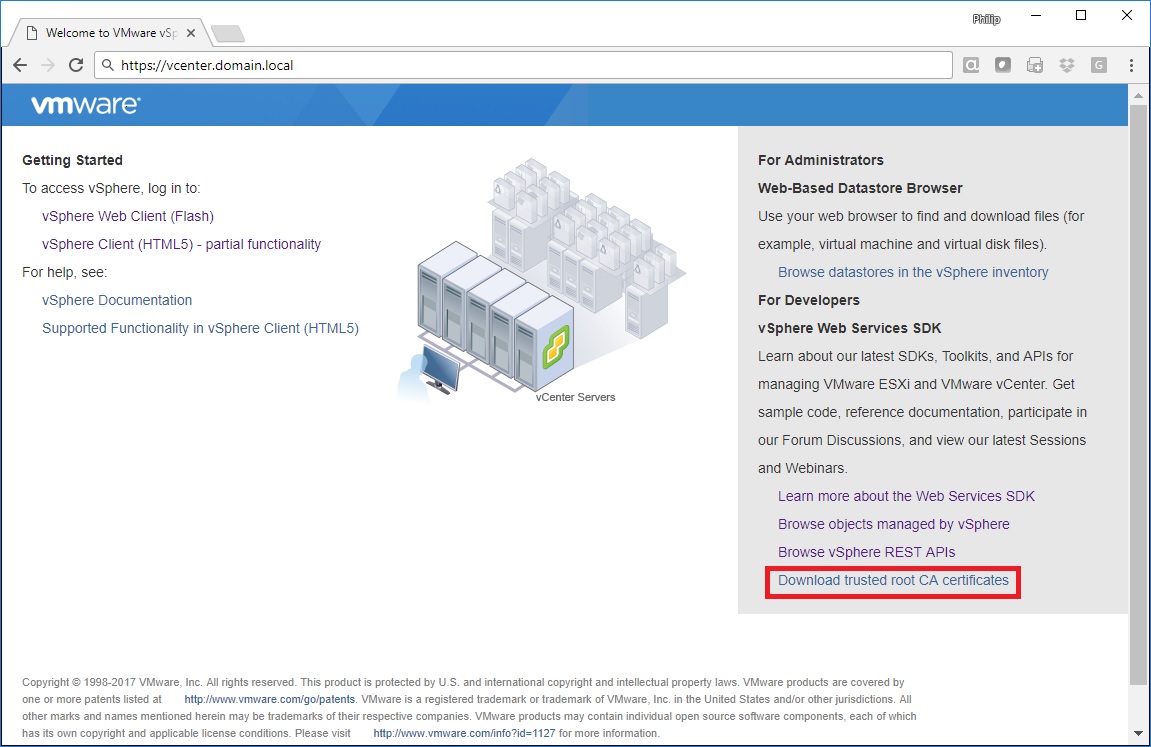
Today when you connect to VCSA you get a web page like this:
or this
Vmware Vsphere Client Mac Os X Download 10 11 4
Ugly, “feels” insecure, gets the security guys all wound up. (and we can’t have that happen!) Let’s get the root certificate from the VCSA and VMCA and install it in the browser so we don’t see these pages anymore.
Get the root certificate
Open up your web browser and go to the VCSA home page. I’ve outlined in red the link you’ll want to click on.
Vmware Vsphere Client Mac Os X Download For Mac
What you’ll get now is a folder in your Downloads folder called “certs”. In that folder are two files. It may also download as a zip file, depending on your browser. You may have to rename the file “download” to “download.zip”.
The file ending in .r0 is the Certificate Revocation List in DER format. You can view the CRL by running
openssl crl –in <filename>.r0 –text –noout
The file ending in .0 is the root CA certificate in PEM format. You can view the CA cert by running
openssl x509 –in <filename>.0 –text –noout
Installing the Root Certificate in the Firefox browser
The root CA is the one we’ll install in our browser. By doing this, the certificate presented by VCSA will chain its root of trust to the imported VMCA root CA certificate.
In Firefox I opened up the certificate list in Advanced settings, selected “Authorities”
I then clicked on Import, selected the .0 file and was presented with this option.
Select “Trust this CA to identify websites” and click OK. Your root CA is now imported and if you open the VCSA web page you’ll find you are no longer presented with the option to verify the certificate. You may need to close and reopen the browser.
The process is similar for other browsers and is well documented for adding the root CA to Windows, Linux and Mac key stores if you prefer to do it that way.
Note: You’ll need to access the VCSA by its FQDN and not its IP address (like I normally do in a lab environment!). Otherwise you’ll get an error like this:
Note that any resource that presents a web page that has its certificate issued by VMCA will now show up as trusted.
For example, host certificates will be valid as well!
Recap
So, to summarize what we’ve learned:
- VCSA now has its own certificate authority called VMCA
- You can install the root certificate of VMCA in your system or browser
- All vSphere components like vCenter, ESXi, solution users, etc can be issued certificates from VMCA if running in Default or Enterprise mode
- VMCA can be bypassed if you don’t want to use it, however you’ll need to do more steps to manage your certificates
- Regardless of which method, all certificates need to be installed into VECS with the exception of ESXi hosts.
- A Certificate Manager tool is provided to help you manage your 3rd party certificate installations
I hope this was helpful. Give it a try in your lab environments and introduce your security people to these new concepts and options. I’ll be curious to hear what they say so send me an email at mfoley at vmware dot com with their feedback!
Thanks for reading,
Mac Os X Download Free
mike
You install VMware Remote Console from the App Store on your macOS machine. Alternatively, you can download an installation package and perform a manual install.
When you install a new version of VMware Remote Console from the App Store, you may be prompted to uninstall any previous versions that were not installed from the App Store.
Verify that your local machine is running a supported version of macOS. For a list of supported operating systems, see the release notes for your version of VMware Remote Console.
Procedure
- To install VMware Remote Console from the App Store, perform the following steps.Note: This procedure is supported for macOS 10.15 and later.
- Open the App Store and search for VMware Remote Console.
- Click Get > Install App.
- If prompted, sign in with your Apple ID and password.
The App Store downloads and installs VMware Remote Console. - To manually install VMware Remote Console, perform the following steps.
- Access the VMware Remote Console download page and download VMware Remote Console for macOS.
You can also access the download page from the vSphere Client or VMware Host Client.
- In the vSphere Client, select any virtual machine, open the Summary tab, and click Launch Remote Console > Download Remote Console.
- In the VMware Host Client, select any virtual machine and select Console > Download VMRC.
- Open the installation package and double-click VMware Remote Console.
- Enter the user name and password of a system administrator.
- Read the terms of the license agreement and click Agree.
- Select whether to join the Customer Experience Improvement Program (CEIP) and click Done.For more information about the CEIP, see Join or Leave the Customer Experience Improvement Program.
- Access the VMware Remote Console download page and download VMware Remote Console for macOS.
VMware Remote Console is installed on your local machine and is configured to open URLs that use the vmrc scheme.